How do I choose an aluminium profile?
Choosing the wrong aluminum profile can lead to structural failures, increased costs, and project delays that no one wants to face. Whether you're designing windows, doors, or industrial frameworks, selecting the right aluminum profiles is crucial for achieving durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide walks you through essential factors including alloy selection, strength requirements, surface finishes, and application-specific considerations to help you make informed decisions that ensure your project's success while avoiding common pitfalls that plague many construction and manufacturing ventures.
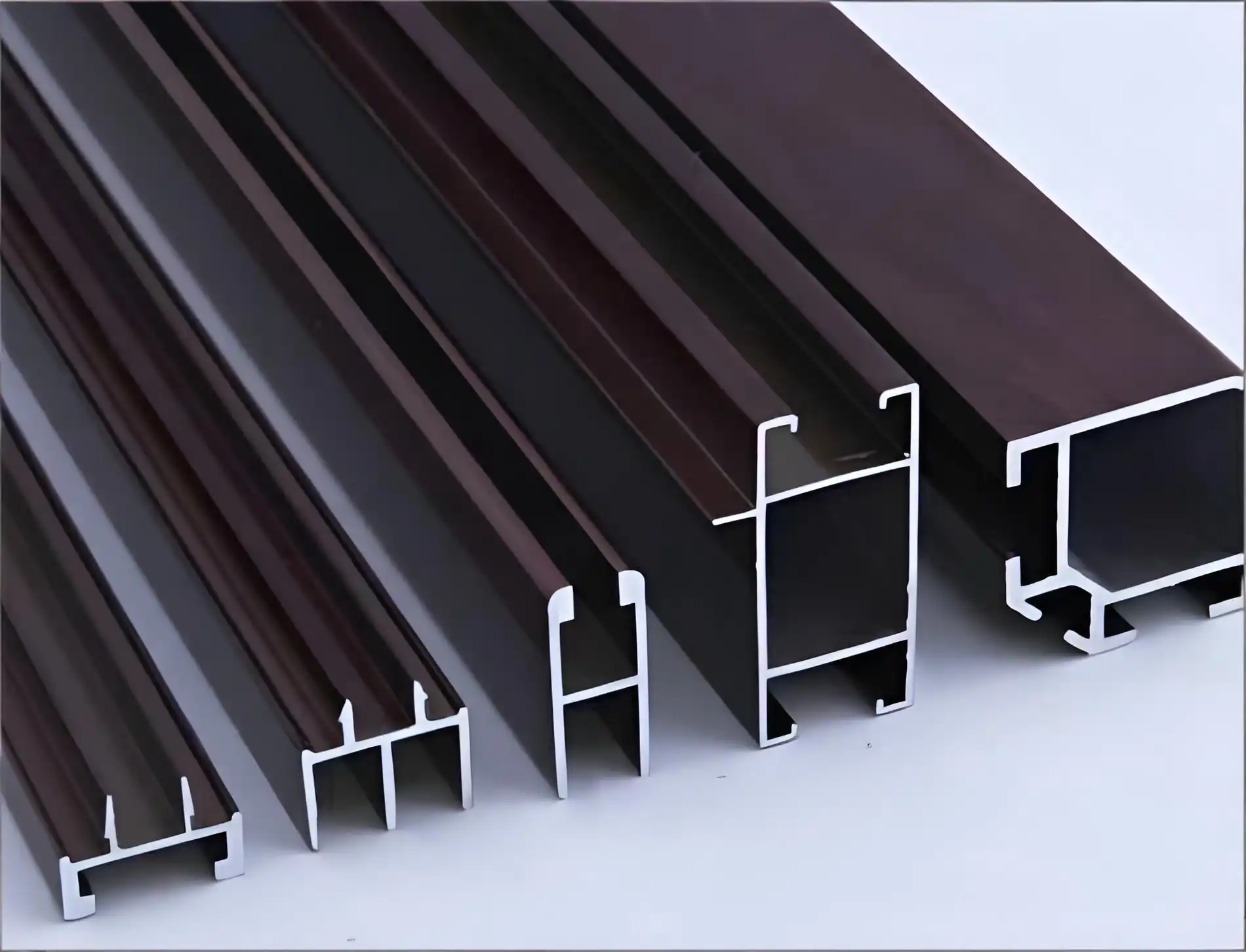
Understanding Aluminum Profiles and Their Importance
Aluminum profiles are extruded aluminum materials with specific cross-sectional shapes created by heating aluminum billets and forcing them through specialized dies. These versatile building materials have revolutionized modern construction and manufacturing due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. The aluminum profile selection process directly impacts your project's structural integrity, longevity, and overall performance. With proper understanding of aluminum profiles, you can optimize material usage while meeting specific load-bearing requirements and environmental conditions. The extrusion process allows manufacturers to create everything from simple flat bars to complex custom shapes that serve architectural, industrial, and decorative purposes across residential buildings, commercial complexes, transportation systems, and specialized equipment applications.
Key Factors in Aluminum Profile Selection

Material Strength and Alloy Type
The mechanical properties of aluminum profiles vary significantly based on their alloy composition and temper designation. When evaluating strength requirements, you must consider both tensile strength and load-bearing capacity for your specific application. Aluminum profiles from the 6063-T5 series offer excellent extrudability and medium strength, making them ideal for architectural applications like window frames and door systems. For higher strength requirements, 6061-T6 aluminum profiles provide superior mechanical properties suitable for structural components and heavy-duty applications. The 7075 series represents one of the strongest aluminum alloys available, though it sacrifices some corrosion resistance. Pure aluminum from the 1100 series offers maximum corrosion resistance but minimal strength, while 5052 aluminum profiles deliver balanced performance for marine and coastal environments. Understanding these distinctions helps you match material properties with application demands, ensuring your aluminum profiles perform optimally under expected loads and environmental stresses.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Considerations
Environmental conditions significantly influence aluminum profile performance and longevity. Corrosion resistance becomes paramount in coastal areas, industrial settings, or regions with extreme weather patterns. Aluminum profiles naturally form a protective oxide layer that prevents further deterioration, but different alloy series offer varying levels of protection. The 1xxx series pure aluminum and 5xxx series alloys demonstrate excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for marine applications and humid environments. Conversely, high-strength 2xxx and 7xxx series aluminum profiles exhibit lower corrosion resistance and may require additional protective coatings. For coastal installations, selecting aluminum profiles with enhanced corrosion protection prevents premature failure and reduces maintenance costs. Climate considerations extend beyond corrosion to include thermal expansion properties, particularly important for large-span applications where temperature fluctuations cause dimensional changes. Thermal break aluminum profiles incorporate non-metallic insulation strips that reduce heat transfer, improving energy efficiency in window and door applications while maintaining structural integrity across temperature variations.
Surface Treatment and Finishing Options
Surface treatments dramatically affect both the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of aluminum profiles. Anodizing creates a hard, corrosion-resistant oxide layer that can be dyed in various colors while maintaining the metal's natural appearance and texture. This electrochemical process penetrates the aluminum surface rather than coating it, providing superior durability and scratch resistance. Powder coating offers virtually unlimited color options and excellent weather resistance, creating a thick protective layer that shields aluminum profiles from UV radiation, moisture, and chemical exposure. For applications requiring reflective or decorative finishes, mechanical polishing creates mirror-like surfaces, while brushing produces distinctive linear patterns. Chemical conversion coatings prepare aluminum profiles for subsequent painting while enhancing corrosion protection. The choice between these treatments depends on your project's aesthetic requirements, environmental exposure, maintenance expectations, and budget constraints. Modern aluminum profiles can combine multiple treatments to achieve optimal performance, such as anodizing followed by clear coating for enhanced weather resistance in demanding applications.
Application-Specific Aluminum Profile Requirements

Architectural and Window Applications
Window and door applications demand aluminum profiles that balance structural strength, thermal performance, and aesthetic appeal. Modern architectural aluminum profiles incorporate thermal break technology that significantly reduces heat transfer between interior and exterior environments, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Multi-chamber designs within aluminum profiles create additional insulation barriers while maintaining the slender profiles that characterize contemporary architecture. For casement windows, aluminum profiles must provide sufficient rigidity to prevent sagging while accommodating hardware and weatherstripping systems. Sliding window applications require aluminum profiles with smooth gliding surfaces and robust corner joints that withstand repeated operation cycles. Folding door systems demand specialized aluminum profiles engineered to support multiple panels while maintaining proper alignment and smooth operation. The wall thickness of architectural aluminum profiles typically ranges from two to three millimeters, providing adequate strength for residential applications, while commercial projects may require heavier sections to meet building codes and wind load requirements.
Industrial and Structural Applications
Industrial applications of aluminum profiles encompass machine frames, conveyor systems, protective enclosures, and modular workstations that benefit from aluminum's lightweight properties and assembly flexibility. Industrial aluminum profiles feature modular dimensions and integrated groove systems that accept standard fasteners, enabling tool-free assembly and easy reconfiguration. The 40x40mm profile size represents the most common industrial standard, offering an optimal balance between rigidity and material economy for medium-duty applications. Light-duty applications utilize 20x20mm or 30x30mm aluminum profiles for equipment housings, control panels, and laboratory furniture where weight reduction is prioritized over load capacity. Heavy-duty industrial frameworks require 60x60mm or 80x80mm aluminum profiles capable of supporting substantial loads in machinery bases, gantry systems, and automated production lines. Profile wall thickness directly influences load-bearing capacity and thread strength for mechanical connections, with thicker walls providing greater stiffness at the expense of increased weight and material costs. Modern aluminum profiles for industrial use often incorporate compatibility with standardized accessories, brackets, and panel mounting systems that accelerate assembly and reduce engineering time.
Technical Specifications and Standards Compliance

Load Calculations and Structural Analysis
Proper aluminum profile selection requires accurate assessment of applied loads, span lengths, and safety factors to ensure structural adequacy. Maximum tensile strength indicates the stress level at which aluminum profiles begin permanent deformation, typically ranging from 95 MPa for 1100 pure aluminum to over 500 MPa for heat-treated 7075 alloys. Engineers must consider both dead loads from the structure's own weight and live loads from occupancy, wind, snow, or operational forces when sizing aluminum profiles. Deflection limits often govern profile selection more than ultimate strength, as excessive flexibility creates functional problems and aesthetic concerns even when structural failure remains unlikely. Second moment of area calculations determine aluminum profile stiffness and resistance to bending under load, with complex cross-sections offering superior performance compared to simple rectangular shapes of equivalent material weight. Safety factors typically range from 1.5 to 3.0 depending on application criticality, environmental uncertainty, and consequences of failure. Finite element analysis software enables detailed stress distribution evaluation for custom aluminum profiles subjected to complex loading patterns.
Quality Standards and Certifications
International standards govern aluminum profile manufacturing to ensure consistent quality, dimensional accuracy, and performance reliability. ISO 9001 certification demonstrates systematic quality management practices throughout production processes from raw material procurement through final inspection and delivery. Aluminum profiles for construction applications must comply with building codes and architectural standards specific to each region, addressing fire resistance, structural performance, and energy efficiency requirements. Testing protocols verify mechanical properties including tensile strength, hardness, and elongation to confirm conformance with specified alloy designations and temper conditions. Surface treatment quality standards ensure adequate coating thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance for anodized and powder-coated aluminum profiles. Dimensional tolerances specified in industry standards typically range from ±0.2mm to ±0.5mm depending on profile complexity and critical features. Reputable manufacturers provide material certifications and test reports documenting chemical composition, mechanical properties, and quality control measures that support project specifications and regulatory compliance requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting appropriate aluminum profiles requires careful evaluation of strength requirements, environmental conditions, surface treatments, and application-specific demands to achieve optimal performance and value. By understanding alloy characteristics, load capacities, and finishing options, you can make informed decisions that ensure project success while avoiding costly mistakes and premature failures.
Cooperate With Hunan Haolv Building Materials Co., Ltd.

Partner with Hunan Haolv Building Materials Co., Ltd., a China Aluminum Profiles manufacturer with over 18 years of expertise delivering superior quality products to 30+ countries worldwide. Our advanced production facilities combine precision CNC cutting, automated assembly systems, and rigorous ISO-certified quality control to produce wholesale Aluminum Profiles that meet international standards. As a trusted China Aluminum Profiles supplier and China Aluminum Profiles factory, we offer comprehensive solutions including customized Aluminum Profiles tailored to your specifications, one-stop product support from frames to accessories, free technical consultation and solution design services, competitive Aluminum Profiles price and detailed Aluminum Profiles Pricelist, plus bulk Aluminum Profiles orders with efficient international logistics. Request your Aluminum Profiles quotation today and experience our 24-hour customer service committed to your project success. Contact us at kristin@haolvwindows.com to discuss your requirements and discover how our proven track record transforms your vision into reality through reliable partnerships built on quality craftsmanship.
References
1. Smith, J. & Williams, R. (2023). "Aluminum Extrusion Technology: Modern Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.
2. Chen, L. (2024). "Structural Performance of Aluminum Profiles in Building Applications." International Journal of Construction Materials.
3. Anderson, M. (2023). "Corrosion Resistance and Surface Treatment of Architectural Aluminum." Materials Science and Technology Review.
4. Zhang, W. & Liu, H. (2024). "Thermal Performance Analysis of Aluminum Window Systems with Thermal Break Technology." Building and Environment Research.
5. Thompson, D. (2023). "Selection Criteria for Industrial Aluminum Profiles: Engineering Considerations and Best Practices." Manufacturing Technology Quarterly.